What is a 5-core cable?
Wat is 5 aderige kabel nu precies? En wat is een ader? Heel simpel, een ader is een draad die beschermd is met een isolatie laag. De laag bestaat vaak uit de materialen: PVC, PE, Plastic of Rubber. This protective layer can be stripped so that the wire becomes visible. For stripping a cable you can use a Cable stripper the wire can consist of the materials: Silver, Gold, Copper or Aluminium.
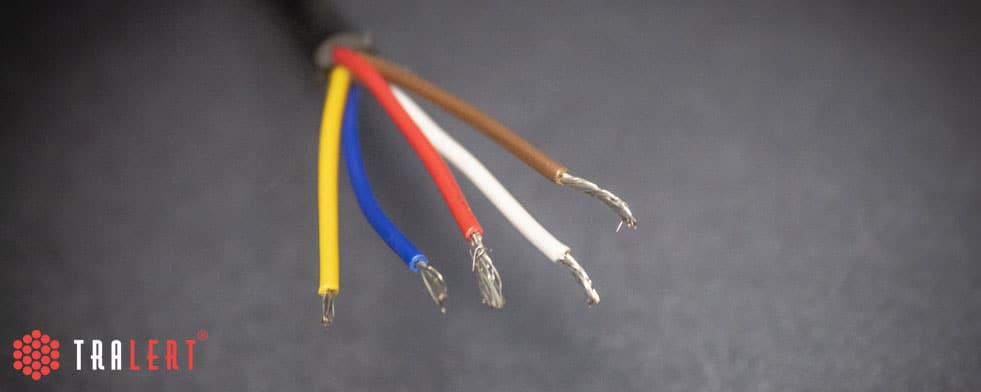
The wires of a 5-core cable
If you look at a (5 core) cable, they almost always consist of several cores and a sheath that holds these cores together. You don't just have 5 core cables but also cables with 3 cores or 8 cores. The core of the cable is the wire that is connected to the connector on, for example, a 5 polige stekker. De kern kan bestaan uit een geleider (van koper) die elektriciteit goed begeleidt. De draad heeft dus een lage weerstand. Er worden verschillende kleuren gebruikt om duidelijk aan te geven wat voor soort functie de draad beheerst. Let op! Leveranciers kunnen gebruik maken van verschillende kleuren. Hierom is het goed de handleiding van de lamp door te lezen. Een andere reden voor het gebruik van deze omhulsels, is het voorkomen dat de draden (aders) contact gaan maken met de andere draden. Als een geleider uit meerdere (koperdraden) draden bestaat, wordt deze ”streng” genoemd (gevlochten draad).
Why copper?
The price of copper varies over time and can therefore be called variable, comparable to raw materials such as gold and oil. However, the beauty of copper is that it is an ideal conductive and flexible material. A lot better than steel or aluminium can. It is a material with a soft texture and is therefore easy to process. This flexibility makes the raw material very suitable for, for example, 5-core cables that are subjected to large mechanical loads while the cable route is in motion. These specifications have made copper the standard material for all cables.
Does temperature also influence conductivity?
Yes, the temperature also affects the conductivity, not only with 5 core cables but with all cables! As the temperature rises, the atoms and electrons gain energy from this. This causes the conductive material to expand. Most metals are better conductors when they are cool. Even at extremely low temperatures, some conductors become superconductors. So conductivity can change the temperature of the material. Electrons therefore flow through conductors without affecting the atoms. Moving electrons experience resistance during the process. This allows an electric current to flow to heat the conducting material.